This is an old revision of the document!

(remove this paragraph once the translation is finished)
Maxim DL
Maxim DL is currently the main interface for controlling the observatory and cameras as well as for performing the observations.
Interface und grundlegende Bedienung
Maxim DL can be started most easily by double-clicking on the icon Maxim DL 6 on the desktop or via the taskbar.
Main window
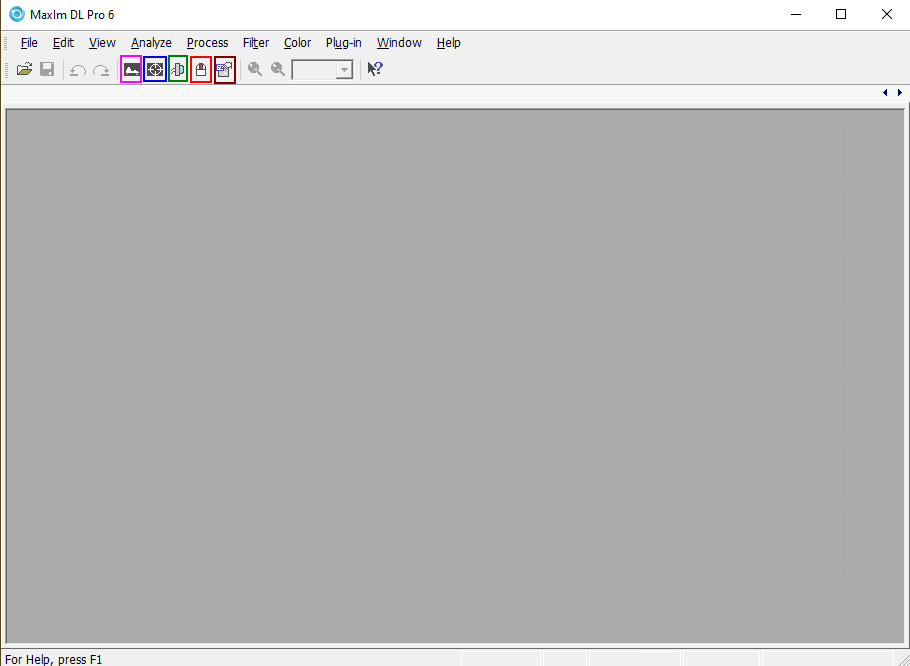
In the picture on the left or below, which shows the main window of Maxim DL, the most important buttons are highlighted. The red button opens the Observatory Panel, which contains the controls for the dome and the telescope. The green button opens the Camera Control Panel, which provides the controls for the cameras. These two windows will be discussed in detail below.
The blue, pink, and brown buttons can be used to display information about the captured images. The header information can be called up via the brown button, while the blue button allows, for example, to display the counts in the individual pixels or in a certain aperture. The pink one makes simple image scaling controls accessible.
Observatory Panel
The Observatory control window has different tabs to control the different parts of the observatory. You can move to objects by entering their coordinates, selecting them from a catalog or marking them on an all-sky map. The dome can be opened, closed, and if necessary moved manually. Furthermore, the telescope can be moved manually via this control window and parked again after the observations are finished.
Setup Tab
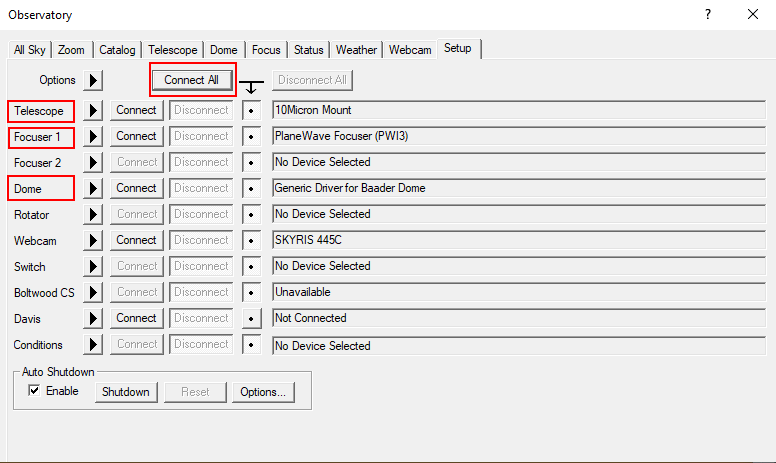
The setup tab is used to establish the connection to the telescope, the dome, and the focuser. You can click on the Connect button behind the respective entry or on Connect All to establish the connection to all components simultaneously. All other entries like Rotator are not relevant for us.
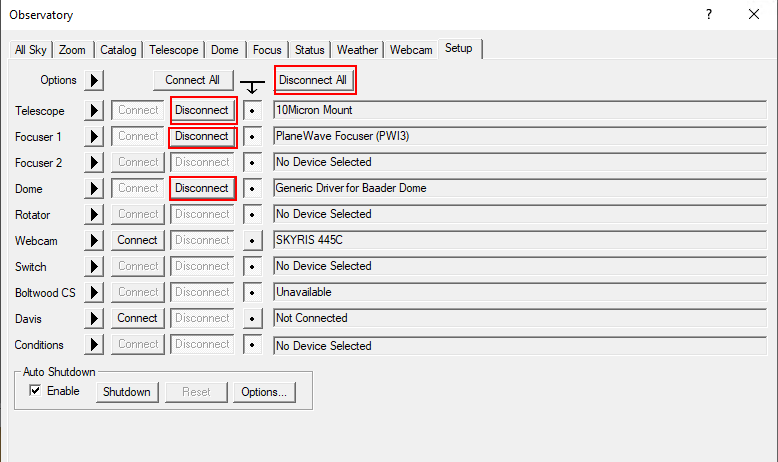
In order to disconnect the devices after the observation, you can click on the individual Disconnect buttons or on Disconnect All.
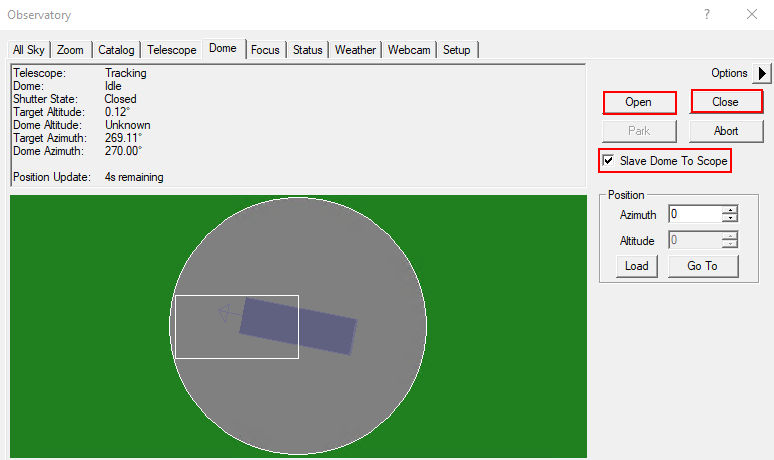
Dome Tab
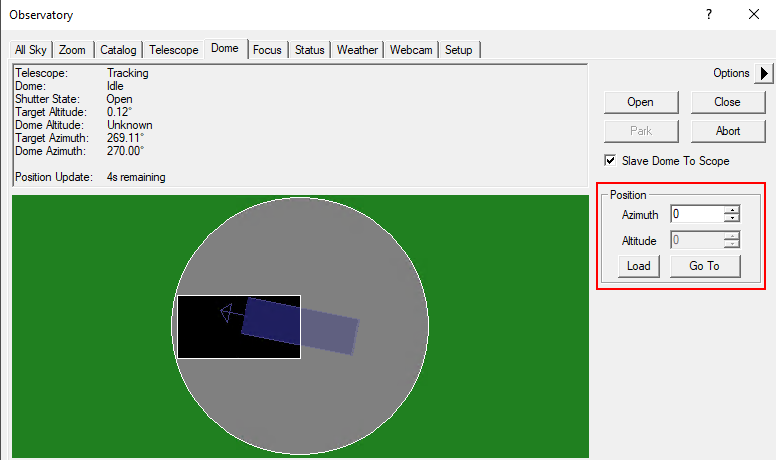
The Open and Close buttons can be used to open and close the dome. The dome always opens or closes completely. It must be ensured that the Slave Dome To Scope option is activated, otherwise the dome will not follow the telescope. Unfortunately, this option turns off every time the dome is opened, closed, or the telescope is parked.
The dome can be moved manually via the functions in the Position box. This is especially useful when the telescope and the slit are not correctly aligned and the dome needs to be recalibrated. On the example shown above, the alignment is not optimal but still so good that the telescope does not look at the dome.
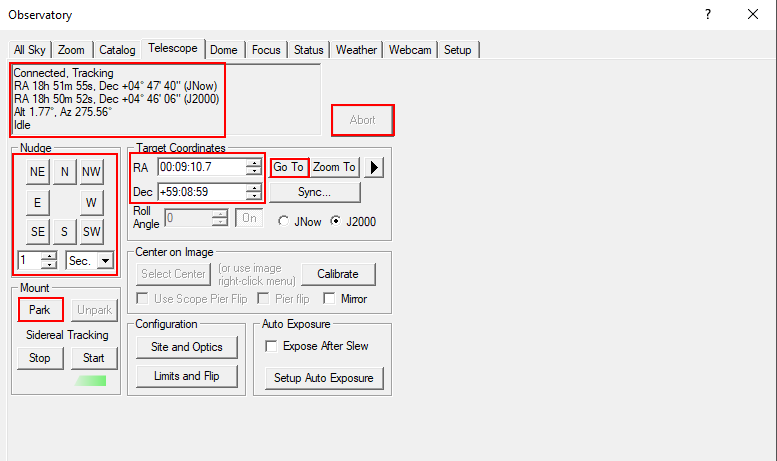
Telescope Tab
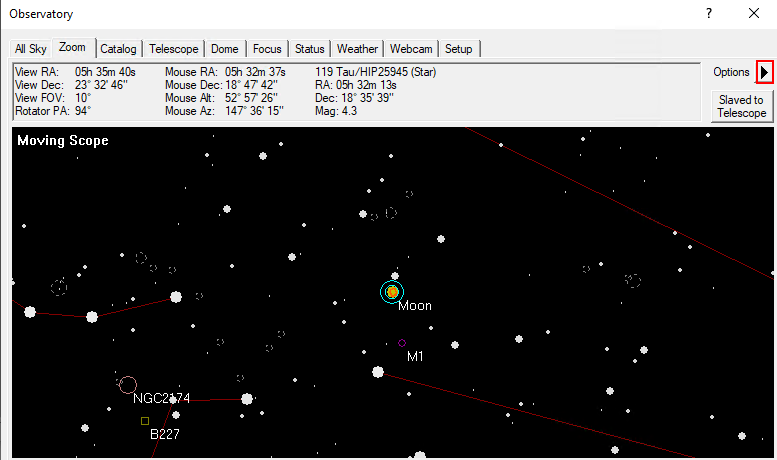
The telescope tab shows in the upper left area where the telescope is currently looking and which action it is currently performing. The right ascension and declination are displayed for the current date as well as for the standard epoch J2000. Furthermore, the altitude above the horizon and the azimuth are displayed. In the example shown below, the telescope is tracking and apart from that is inactive.
The buttons in the Nudge section can be used to move the telescope manually, with the step size selected via the drop-down menus. Each movement can again be aborted via the Abort button.
In the Target Coordinates area you can enter the right ascension and declination of an object and slew to it via the Go To button. The Zoom To button switches to the Zoom tab, which displays a map of the sky at the respective coordinates.
The Park button in the Mount area can be used to park the telescope after the observation.
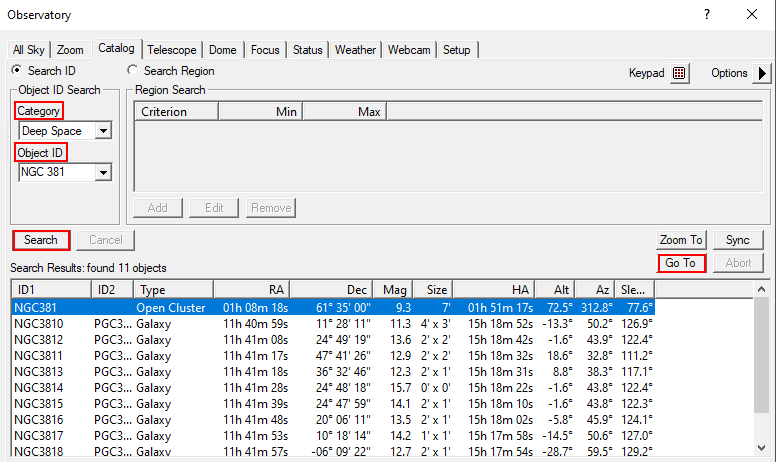
Catalog Tab
Using the Catalog tab, the built-in catalogs can be searched for objects. To do this, first select a category from the Category drop-down menu. You can choose between Stars, Deep Space and Solar System. From the drop-down menu Object ID either the object directly or a catalog can be selected. In the latter case the catalog number of the object, or only a part of it, can be entered (see example below). After a click on Search a list of possible objects is displayed. The desired object can be selected from this list. With a click on Go To the object is approached.
Zoom Tab
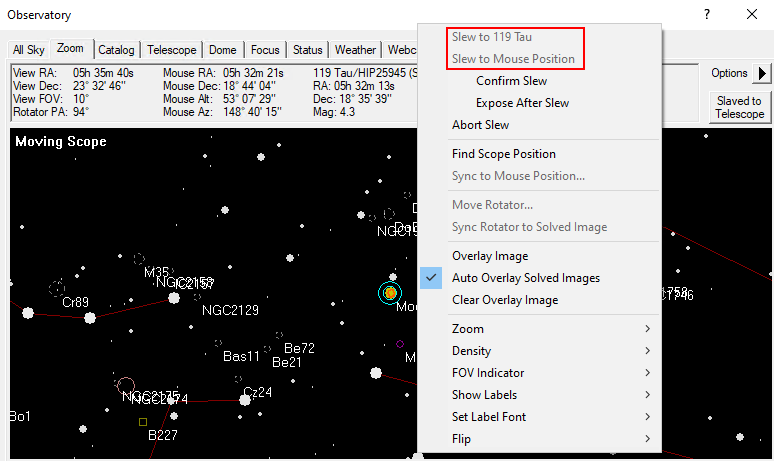
In the zoom tab, the sky map around the selected object is displayed. Via the option button (arrow) on the right and via the context menu, many options are accessible, such as the zoom level. If one clicks with the right mouse button on any point of the map, one can slew the telescope to this point via Slew to Mouse Position. If you click on an object, it can be selected directly. In the example below the corresponding option is Slew tp 119 Tau.
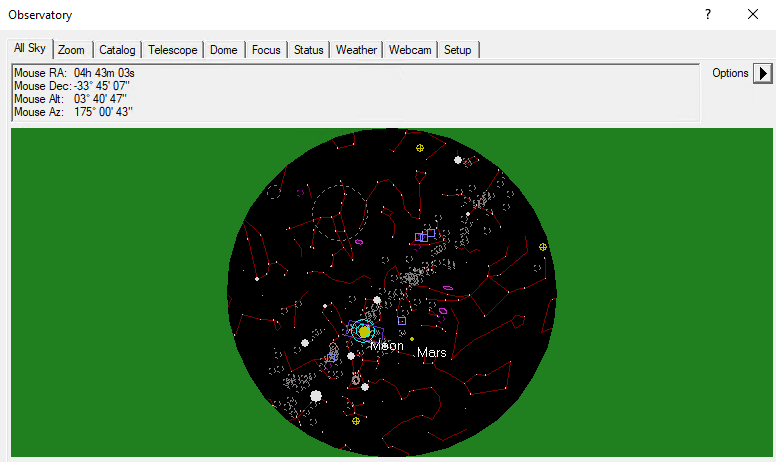
Der All-Sky-Tab
Der All-Sky-Tab zeigt den aktuellen Himmel. Über einen Rechtsklick kann z. B. in einen beliebigen Bereich gezoomt werden. In dem Fall wechselt man automatisch zum Zoom-Tab. Über den Optionsbutton (Pfeil) rechts sind wiederum viele Einstellungsoptionen zugänglich.
Camera Panel
Über das Camera Control-Fenster können die Kameras gesteuert werden und die Aufnahmen angefertigt werden.
Der Setup-Tab
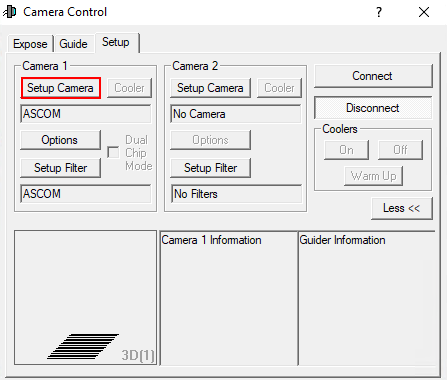
Wie der Name schon sagt dient dieses Fenster dem Verbinden der Kameras mit Maxim DL. Dies gestaltet ich für jeden Kamerahersteller leicht unterschiedlich. Hier gehen wir auf die Vorgangsweise für QHYCCD-Kameras sowie für SBIG-Kameras ein, da diese bei uns in erster Linie eingesetzt werden. Für jedes Kameramodell muss zuerst der entsprechende Treiber ausgewählt werden. Dies muss sowohl für die eigentliche Kamera als auch für das Filterrad gemacht werden. Soll eine Guidingkamera verwendet werden muss auch diese hier verbunden werden. Normalerweise wird die Guidingkamera als Camera 2 verbunden, während die Hauptkamera dementsprechend als Camera 1 angebunden wird.
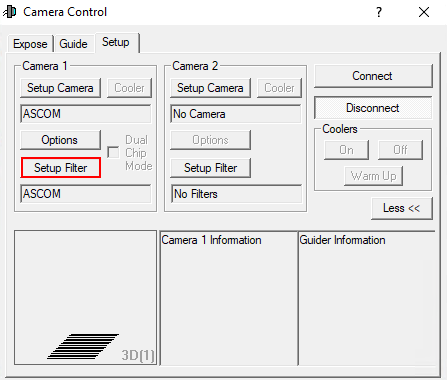
Als erstes klickt man unabhängig vom Hersteller auf Setup Camera.
Verbinden von QHYCCD-Kameras:
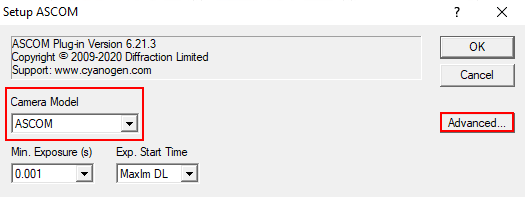
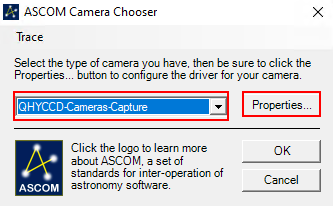
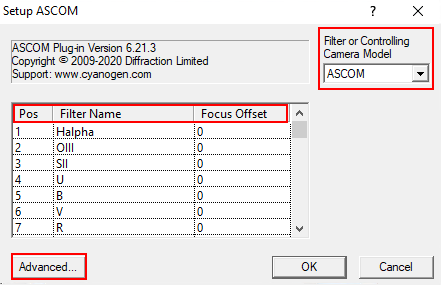
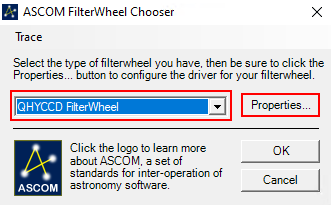
In dem sich öffnenden Fenster wählt man in dem Dropdown-Menü Camera Model ASCOM aus und klickt danach auf Advanced… (Schritt 1). Danach öffnen sich ein weiteres Fenster. In diesem wählt man wiederum über das Dropdown-Menü QHYCCD-Cameras-Capture aus und klickt anschließend auf Properties… (Schritt 2). Danach öffnet sich das Einstellungsmenü für den ASCOM-Treiber für die QHYCCD-Kameras. ASCOM ist die grundlegende Schnittstelle über die viele Funktionen des Observatoriums laufen.
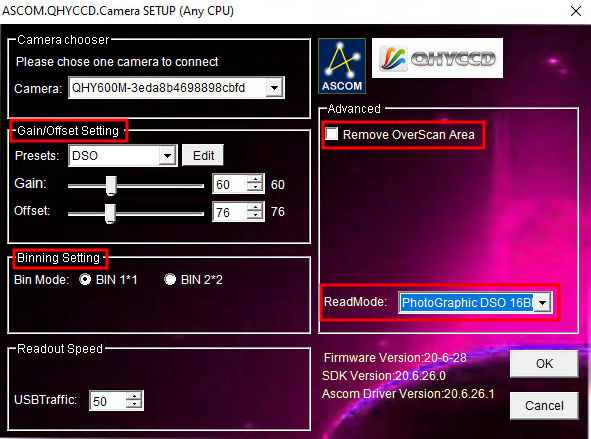
Im letzten Schritt (3) können nun alle wichtigen Einstellungen für den ASCOM-Treiber gemacht werden. Hierzu zählen der Auslesemodus, welcher über das Dropdown-Menü ReadMode ausgewählt werden kann. Zur Auswahl stehen: PhotoGraphic DSO 16bit, High Gain Mode 16bit, Extend Fullwell Mode und Extend Fullwell 2CMS. Unter Gain/Offset Setting kann dann der Gain und Offset eingestellt werden. Diese Einstellungen können unter Preset gespeichert werden bzw. gespeicherte Einstelllungen auch abgerufen werden. Zusätzlich sollte für wissenschaftliche Aufnahmen auch die Option Remove Overscan Area aktiviert werden. Anschließend können alle drei Fenster durch Klicke auf OK geschloßen werden.
Verbinden von QHYCCD-Filterrädern:
Zum verbinden eines Filterrades klickt man zuerst auf Setup Filter.
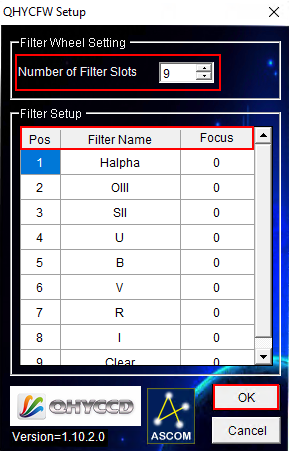
Im ersten Schritt muss aus dem Dropdown-Menü Filter or Controlling Camera Model ASCOM ausgewählt werden. Anschließend klickt man auf Advanced…. In dem sich öffnenden Fenster wählt man aus dem Dropdown-Menü QHYCCD FilterWheel aus und klickt danach auf Properties… (Schritt 2). Daraufhin öffnet sich ein weiteres Fenster, welches die möglichen Treibereinstellungen zeigt. Die Einstellungen in diesem Fenster müssen in der Regel nur einmalig vorgenommen werden. Auszuwählen sind die Number of Filter Slots (in unserem Fall sind das 9) und die jeweiligen Filternamen sowie etwaige Korrekturen für den Fokus (Schritt 3). Danach müssen alle drei Fenster durch einen Klick auf OK bestätigt und geschlossen werden.
Verbinden von SBIG-Kameras:
Kommt noch…
Verbinden von SBIG-Filterrädern:
Kommt noch…
Finaler Schritt:
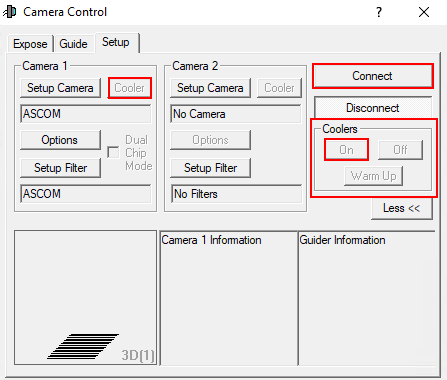
Nun muss noch auf Connect geklickt werden. Anschließend kann unter Coolers die Kühlung aktiviert und unter Cooler die Zieltemperatur eingestellt werden.
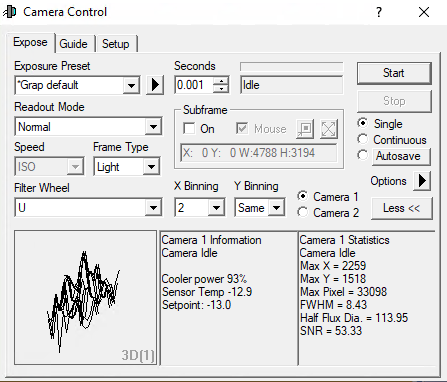
Der Expose-Tab
In diesem Tab findet man, auf kleinem Raum, die wichtigsten Einstellung rund um die Aufnahme der Bilder. Eigene und bereits vordefinierte Einstellungssets können unter Exposure Preset gefunden bzw. neu angelegt werden. Die wichtigste Einstellung ist die Belichtungszeit (Seconds). Rechts daneben findet sich die Statusinformationszeile, welche anzeigt was die Kamera aktuell tut. Im unteren Beispiel ist die Kamera inaktiv (Idle).
Die Filter sind unter Filter Wheel zu finden. Die Binning-Optionen sind wiederum über die beiden Dropdown-Menüs X Binning und Y Binning zugänglich. Des Weiteren kann der Auslesemodus (Readout Mode) ausgewählt werde, was z. B. für die QHY600M wichtig ist. Über die Optionen Single, Continuous und Autosave sind als grundlegenden Modi auswählbar. Beim ersten wird nur eine einzelne Aufnahme angefertigt, wohingegen beim letzten ganze Aufnahmeserien erstellt werden können. Beim Modus Continuous werden hintereinander Aufnahmen mit der eingestellten Belichtungszeit erstellt und dargestellt. Dieser Modus eignet sich besonders gut zum Fokussieren. In dem entsprechenden Artikel gehen wir auch genauer auf die unteren 3 Paneele ein. Weitere Optionen sind noch über Options (Pfeilbutton) zugänglich.
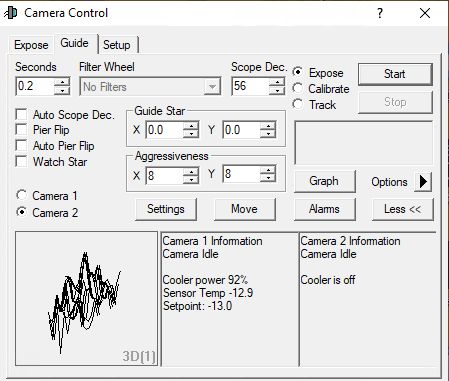
Der Guide-Tab
Der Guide-Tab wiederum hält die wichtigsten Einstellungen für das Guiding des Teleskops bereit. Auf die Details gehen wir in einer Kurzanleitung zum Guiding ein.
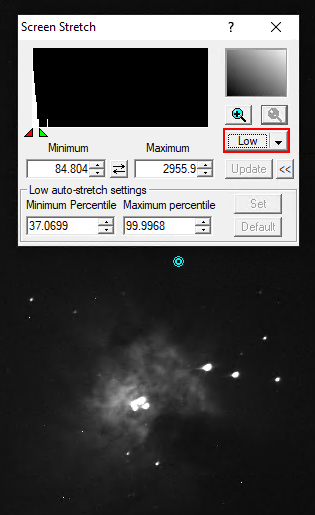
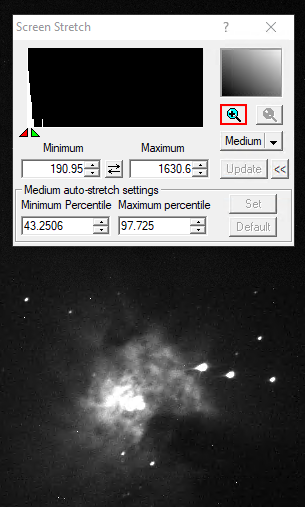
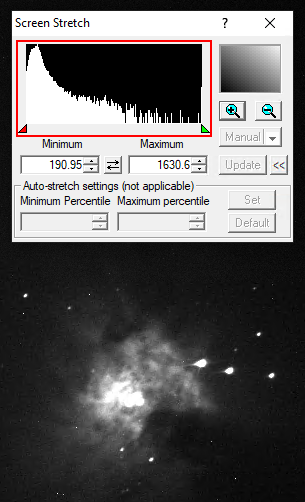
Screen Stretch Panel
Über das Screen Stretch Panel kann die Skalierung der Aufnahmen beeinflusst werden. Im ersten Beispiel unten, welches M42 zeigt, ist die Skalierung auf Low gestellt. Erhöht man die Skalierung auf Medium werden deutlich mehr Details von M42 sichtbar. Viele weitere hilfreiche vordefinierte Skalierungen können aus dem entsprechenden Dropdown-Menü ausgewählt werden.
Klickt man auf das Plus-Symbol im oberen rechten Bereich, wird in das oben links dargestellte Histogramm gezoomt. Dies ermöglicht es die Skalierung über das rote und das grüne Dreieck feiner einzustellen, wobei das rote Dreieck den Schwarzwert und das grüne Dreieck des Weißwert definiert. Entsprechendes kann auch über die Felder Minimum und Maximum erfolgen.
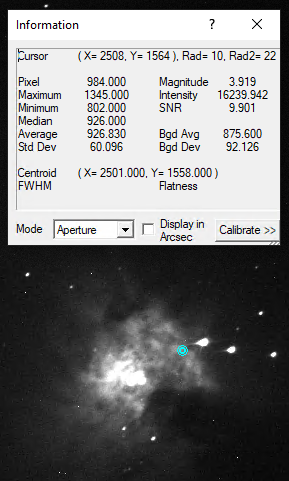
Information Panel
Das Information Panel ist insbesondere hilfreich um zu prüfen, ob das Bild überbelichtet ist und herauszufinden an welchen Sternen dies unter Umständen liegt. Hier sind für uns insbesondere die Werte Pixel und Maximum interessant. Im Standardmodus Aperture werden die Informationen aus der auf dem Bild dargestellten türkisen Apertur ausgelesen, welche man z.B. aber auch auf einen hellen Stern schieben kann. Tut man dies sind z.B. noch das Signal-Rausch-Verhältnis (SNR) und die Full-Width-Half-Maximum (FWHM) von Interesse. Werte wie die Magnitude sind auf unseren zumeist unkalibrierten Bildern nicht von Relevanz.